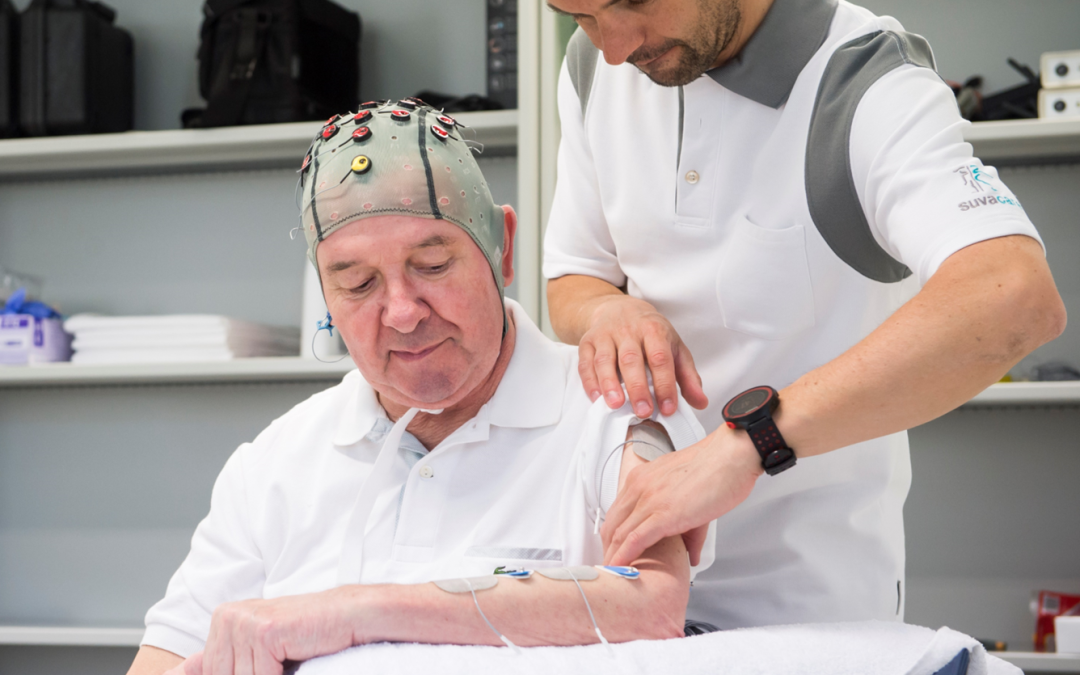
Non-invasive brain stimulation (NIBS) techniques, such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), are increasingly being used in stroke rehabilitation to enhance recovery and neuroplasticity. NIBS promotes brain plasticity, helping rewire neural pathways that may have been damaged by the stroke. TMS and tDCS can increase or decrease cortical excitability, which may aid in restoring function to affected areas. Targeting the motor cortex, for example, can improve hand and arm function. NIBS can also target areas involved in cognition, potentially helping with memory, attention, and executive functions after a stroke. Thoses techniques can also be used to stimulate language centers in the brain for aphasic patients. Non-invasive brain stimulation represents a promising adjunct to traditional stroke rehabilitation methods. By harnessing the brain’s capacity for change, NIBS can support recovery processes and improve quality of life for stroke survivors. One part of the pilot 3 of the SUN project will rely on these technologies in order to optimize patients’ recovery.
Don’t forget to follow SUN XR on social media.